Adult, Paediatric & Neonatal 2 to 150 bpm
Neonates: 2 to 100 ml, Pediatric: patients 20 to 300 ml
Pressure to controlled ventilation: PC to CMV, PC to AC, PC to SIMV, PC to PSV, PC to MMV, PC to APRV;
Refurbished Drager Babylog VN500 Ventilator - Teaching Unit
The Dräger Babylog VN500 is a neonatal ventilator. This is a complete, integrated ventilation solution that is designed with the latest technology. It features a user-friendly interface, extended monitoring functions, and smart data visualizations.
Advancing Neonatal Ventilation Technology
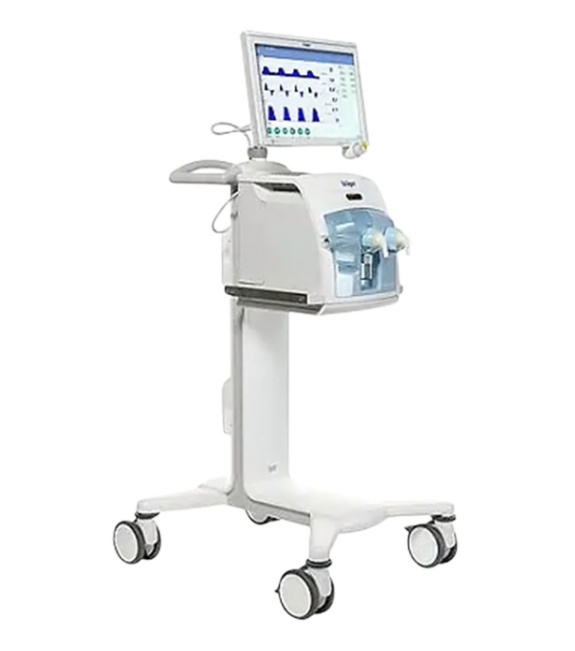
CONFIGURABLE USER INTERFACE AND MONITORING TOOLS
Individual monitoring views that can be determined by the user
Standardized, intuitive and user-friendly graphical user interface
Online help including context-sensitive help functions
Extended monitoring functions and smart data visualization
DECISION-MAKING TOOLS THAT DECREASE COGNITIVE WORKLOAD
Smart Pulmonary View provides a graphical display of the compliance and resistance, including spontaneous breathing
Trending, measured parameters, waveforms and loops
WORKSTATION FUNCTIONS
Configuration to suit your needs
Downloadable screenshots for training, research and knowledge transfer
Fast, standard configuration of all Babylog VN500 devices via USB
Ability to connect the C500 Cockpit display to an overhead projector
Several log export options to support learning and research
3 RS-232 data ports for information sharing to central database systems
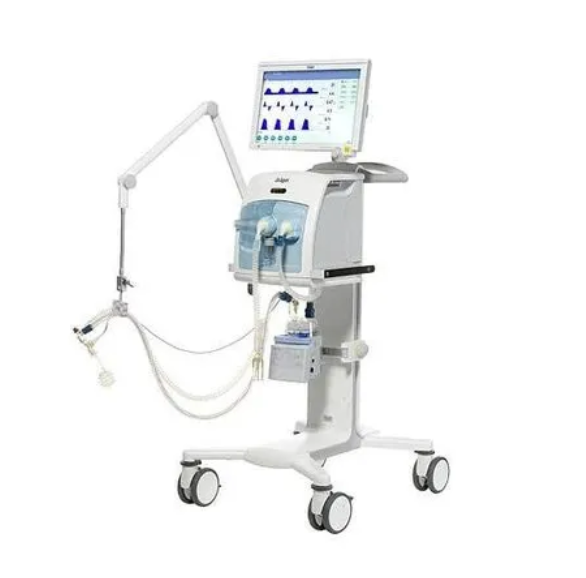
WORKSTATION FUNCTIONS
Original Dräger leak adaptation and leak compensation technology to maintain sensitive triggering and volume targets
PC-MMV can be used for weaning and promotes spontaneous breathing and automatically adapts support in line with patient needs
Integrated non-invasive ventilation and high-flow oxygen therapy
Specifications
| Ventilation Modes | Pressure-controlled ventilation: | Support of spontaneous breathing: |
PC-CMV PC-AC PC-SIMV PC-PSV PC-MMV PC-APRV | SPN-CPAP/PS SPN-CPAP/VS SPN-PPS SPN-CPAP | |
| Enhancements | Babylog VN500 and Infinity® C500: 420 × 685 × 410 mm (11.5 × 12.6 × 16.1 in) | Babylog VN500 and Infinity® C500 on trolley: 577 × 1400 × 677 mm (22.7 × 55.1 × 26.7 in) |
| Weight | Babylog VN500 and Infinity® C500: 25 kg (55.1 lbs) Babylog VN500 and Infinity® C500 on trolley: 59 kg (130 lbs) GS500: 10.5 kg (23 lbs) | PS500: 27 kg (59.5 lbs) Mounting Adapter for 38 mm pole: 2.35 kg (5.18 lbs) |
enu navigation and alarm silencing.
The Babylog VN500 has a unique interface for monitoring the patient’s pulmonary status, called Smart Pulmonary View . This is a graphic display of the compliance and resistance as well as of the spontaneous and mandatory minute volume.
Pressure Control Assist Control
Mandatory breaths: Machine triggered (preset frequency) or patient triggered (flow sensitivity) and machine cycled (inspiratory time)
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set PEEP, frequency, inspiratory pressure, rise time, and inspiratory time
Spontaneous breaths: Permitted during mandatory breath but not between mandatory breaths
Between-breath targets: None
Pressure Control Assist Control with Volume Guarantee
Mandatory breaths: Machine triggered (preset frequency) or patient triggered (flow sensitivity) and machine cycled (inspiratory time)
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set PEEP, frequency, rise time, and inspiratory time
Ventilator-set inspiratory pressure
Spontaneous breaths: Permitted during mandatory breath but not between mandatory breaths
Between-breath targets: Operator-set tidal volume
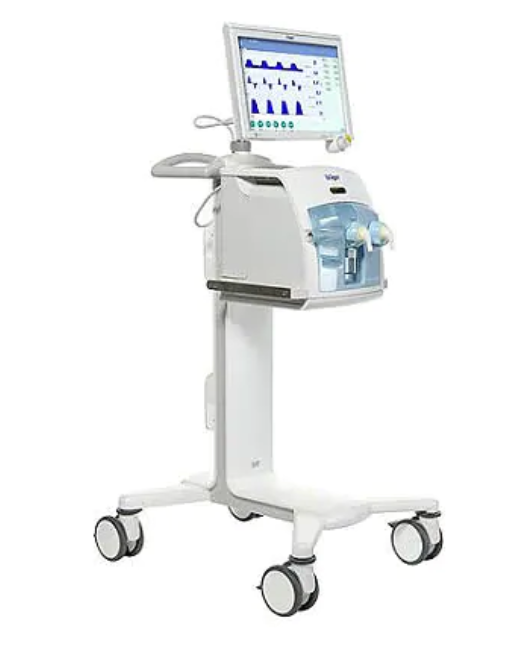
Pressure Control Airway Pressure Release Ventilation
Mandatory breaths: Machine triggered (preset frequency) and machine cycled (inspiratory time). Patient triggering of mandatory breaths is possible using the AutoRelease feature. This triggers inspiration once a preset expiratory flow threshold is reached. When AutoRelease is turned on, the switch from PHigh to PLow is synchronized with the patient’s breathing. Thus, with AutoRelease, what were formerly machine-triggered and machine-cycled (mandatory) breaths are converted to patient-triggered and patient-cycled (spontaneous) breaths.
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set PEEP (called PLow), peak inspiratory pressure (called PHigh), rise time, inspiratory time (called THigh), and expiratory time (called TLow). The inspiratory trigger sensitivity may also be set (using AutoRelease) as a percentage of peak expiratory flow.
Spontaneous breaths: Patient triggered (flow sensitivity) and patient cycled (% peak inspiratory flow). Spontaneous breaths are permitted both between and during mandatory breaths.
Within-breath settings:
Automatic tube compensation
Between-breath targets: None
Pressure Control Continuous Mandatory Ventilation
Mandatory breaths: Machine triggered (preset frequency) and machine cycled (inspiratory time) and patient trigger efforts are ignored. Spontaneous breaths are permitted both between and during mandatory breaths. Because of this feature, the mode is classified as a form of intermittent mandatory ventilation, not continuous mandatory ventilation, despite the name given by Dräger.
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set PEEP, frequency, inspiratory pressure, rise time, and inspiratory time
Spontaneous breaths: Patient triggered (flow sensitivity) and patient cycled (% peak inspiratory flow)
Within-breath settings:
None
Between-breath targets: None
Pressure Control Mandatory Minute Volume Ventilation with Volume Guarantee
Mandatory breaths: Machine triggered (preset frequency) or patient synchronized (flow sensitivity) and machine cycled (inspiratory time). Mandatory breaths are suppressed if minute ventilation from spontaneous breaths is above preset minute ventilation target (i.e., product of tidal volume and frequency).
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set PEEP, frequency, rise time, and inspiratory time
Ventilator-set inspiratory pressure
Spontaneous breaths: Patient triggered (flow sensitivity) and patient cycled (% peak inspiratory flow)
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set inspiratory pressure and rise time
Between-breath targets: Operator-set tidal volume. The settings for tidal volume and frequency constitute a between-breath target for minimum minute ventilation. Mandatory breaths are suppressed if minute ventilation from spontaneous breaths is this target.
Pressure Control Pressure Support Ventilation
Mandatory breaths: Machine triggered (preset frequency) and patient cycled (% peak inspiratory flow)
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set PEEP, frequency, inspiratory pressure, and rise time
Spontaneous breaths: Patient triggered (flow sensitivity) and patient cycled (% peak inspiratory flow)
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set inspiratory pressure and rise time
Between-breath targets: None
Pressure Control Pressure Support Ventilation with Volume Guarantee
Mandatory breaths: Machine triggered (preset frequency) and patient cycled (% peak inspiratory flow)
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set PEEP, frequency, and rise time
Ventilator-set inspiratory pressure
Spontaneous breaths: Patient triggered (flow sensitivity) and patient cycled (% peak inspiratory flow)
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set rise time
Ventilator-set inspiratory pressure
Between-breath targets: Operator-set tidal volume
Spontaneous Continuous Positive Airway Pressure/Pressure Support
Mandatory breaths: Not allowed
Spontaneous breaths: Patient triggered (flow sensitivity) and patient cycled (% peak inspiratory flow)
Within-breath settings:
Operator-set inspiratory pressure and rise time
Between-breath targets: None